-
When developing with Microsoft IDE's, please DO NOT USE PRE-COMPILED HEADERS for broad cross platform support.
i.e. Don't use stdafx.h on MS/Windows if you are going to port it to platforms which do not support it (or use defines to mask it out). It doesn't always work on non-Microsoft platforms as it is not part of the C++ standard.
After creating the MS/Visual C++ project select:- "Project" + "Settings" + "C++" tab:
- Category: "Precompiled Headers". Check "not using precompiled headers"
Note that the GNU gcc/g++ compiler now supports precompiled headers. If you plan on only supporting Visual C++ and GNU C/C++, the support is available.
See GNU pre-compiled headers documentation. -
Using the editor in MS/VC++ will sometimes remove the line terminator on the last line, as perceived by UNIX.
You might want to leave a blank line at the end of your files. Not just a carriage return but an actual blank space on the last line to avoid compiler errors.
Appending a blank line at the end of the file will fix this compiler warning:
Main.h:55:7: warning: no newline at end of file - PITFALL: MS/Visual studio will add ^M (control M) as a line
termination. It has been used by some to edit UNIX shell scripts. The
first line of a UNIX shell script denotes the shell used.
#!/bin/bashAfter editing with Microsoft IDE:
When trying to execute the shell script the system responds vaguely:
#!/bin/bash^M
": bad interpreter: No such file or directory" -
Using VI to "clean" or "restore" a source code file to usibility:
Remove ^M:
:1,$ s/^V^M//Repair Tab indentation. MS/VC++ uses a tab to represent 4 spaces of indentation (default). Most other systems use a Tab to represent 8 spaces.
Turn Tabs into four blank spaces to remove abiguity and restore indentation:
:1,$ s/^VTab/ /g -
Use white spaces for indentation instead of Tabs:
- Visual C++ 6.0: Select "Tools" + "Options..." +
the tab marked "Tabs". Select the option "Insert spaces" to avoid the
automatic insertion of tabs for indentation.
this will be applied to all files for "File type:" "Default".
Select the "OK" button. - Visual Studio 7.1: Select "Tools" +
"Options...". Select from the tree the folder "Text Editor" + "C/C++"
(or which ever type is suitable) + "Tabs".
Select the radio button "Insert Spaces"
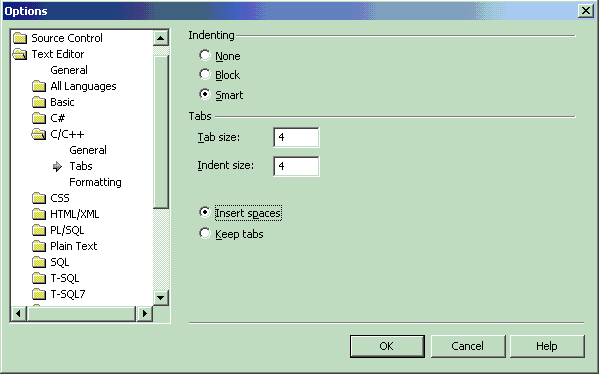
- Visual C++ 6.0: Select "Tools" + "Options..." +
the tab marked "Tabs". Select the option "Insert spaces" to avoid the
automatic insertion of tabs for indentation.
this will be applied to all files for "File type:" "Default".
-
Restore or "repair" sections of code indented by tabs:
- Select code to "restore". (ctrl-a for the whole file)
- Select "Edit" + "Advanced" + "Untabify Selection"
-
Tip to view white spaces in file:
Select "Edit" + "Advanced" + "View white space"
or
- Visual C++ 6.0: Ctrl+Shift+8
- Visual Studio 7.1: Ctrl-R, Ctrl-W
-
Use define macros to fix MS/Windows platform dependancies: (i.e.)
#ifdef WIN32
char *file_system_root = "C:\\";
char *dir_separator = "\";
#else
char *file_system_root = "/";
char *dir_separator = "/";
#endifIf using GTK+ cross platform API you can also use the C macro G_DIR_SEPARATOR.
And vice-versa:
#ifndef WIN32
#include <syslog.h>
#endif - If using the Subversion CM system, configure Subversion to remove "^M" upon check-in. See the YoLinux Tutorial: Subversion Server and Trac Server Installation and Configuration.
My choice is to avoid the Microsoft IDE editor altogether but if you insist, please be aware of the previous pitfalls and fixes. Here are a list of Linux C++ IDEs (some are cross platform).
- Don't name include files aux.h, com1.h, com2.h or prn.h. Visual C++ prohibits using include files with the same root name as default device names. In fact it will not like "aux.anything", etc.

