| File | Description |
|---|---|
| /etc/resolv.conf | List DNS servers for internet domain name resolution. Manual page for: /etc/resolv.conf |
| /etc/hosts | Lists hosts to be resolved locally (not by DNS). Manual page for: /etc/hosts |
| /etc/nsswitch.conf | List order of host name search. Typically look at local files, then NIS server, then DNS server. Manual page for: /etc/nsswitch.conf |
| Red Hat/Fedora/CentOS: /etc/sysconfig/network | Specify network configuration. eg. Static IP, DHCP, NIS, etc. |
| Red Hat/Fedora/CentOS: /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-device | Specify TCP network information. |
| Ubuntu/Debian: /etc/network/interfaces | Specify network configuration and devices. eg. Static IP and info, DHCP, etc. |
The following files configure the system so that host names can be resolved. This is required when one will ssh to a host name eg. venus.megacorp.com or point an email client to smtp.megacorp.com. The system must be able to resolve the host names to IP addresses so that the network connection can be made.
- File: /etc/resolv.conf - host name resolver configuration file to define server responsible for name resolution
search name-of-domain.com - Name of your domain or ISP's domain if using their name server nameserver XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX - IP address of primary name server nameserver XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX - IP address of secondary name serverThis configures Linux so that it knows which DNS server will be resolving domain names into IP addresses. If using DHCP client, this will automatically be sent to you by the ISP and loaded into this file as part of the DHCP protocol. If using a static IP address, ask the ISP or check another machine on your network.
Red Hat/Fedora GUI: /usr/sbin/system-config-network (select tab "DNS"). - File: /etc/hosts - locally resolve node names to IP addresses by explicit definition
127.0.0.1 your-node-name.your-domain.com localhost.localdomain localhost XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX node-nameNote when adding hosts to this file, place the fully qualified name first. (It helps sendmail identify your server correctly) i.e.:XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX superserver.yolinux.com superserver
This informs Linux of local systems on the network which are not handled by the DNS server. (or for all systems in your LAN if you are not using DNS or NIS)
The file format for the hosts file is specified by RFC 952.
Red Hat/Fedora configuration GUI: /usr/sbin/system-config-network (select tab "Hosts").
- File: /etc/nsswitch.conf - System Databases and Name Service Switch configuration file. Define the cascading priority of name resolvers
hosts: files dns nisplus nisThis example tells Linux to first resolve a host name by looking at the local hosts file (/etc/hosts), then if the name is not found look to your DNS server as defined by /etc/resolv.conf and if not found there look to your NIS server.In the past this file has had the following names: /etc/nsswitch.conf, /etc/svc.conf, /etc/netsvc.conf, ... depending on the distribution.
Note that device configuration information can be found in the autogenerated file /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
Files which hold the Linux system network configuration:
- /etc/sysconfig/network
Red Hat network configuration file used by the system during the boot process.
- File: /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
Configuration settings for your first ethernet port (0). Your second port is eth1. - File:
- /etc/modprobe.conf (kernel 2.6)
- /etc/modules.conf (kernel 2.4)
- (or for older systems: /etc/conf.modules)
alias eth0 eepro100
Modules for other devices on the system will also be listed. This tells the kernel which device driver to use if configured as a loadable module. (default for Red Hat)
The following GUI tools edit the system configuration files. There is no difference in the configuration developed with the GUI tools and that developed by editing system configuration files directly.
TCP/IP ethernet configuration:
- Network configuration:
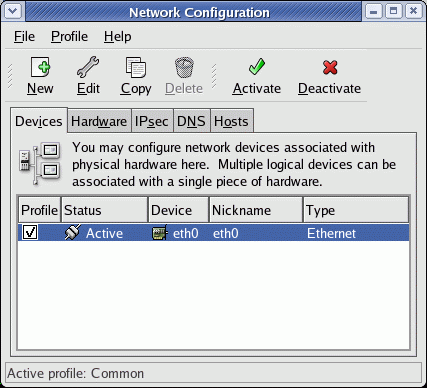
/usr/sbin/system-config-network (FC-2/3) GUI shown here --->
/usr/bin/redhat-config-network (/usr/bin/neat) (RH 7.2+ FC-1) - Text console configuration tool:
/usr/sbin/system-config-network-tui (Text User Interface (TUI) for Fedora Core 2/3)
/usr/bin/redhat-config-network-tui (RH 9.0 - FC-1) - Text console network configuration tool.
First interface only - eth0: /usr/sbin/netconfig - /usr/bin/netcfg (GUI) (last available with RH 7.1)
- Gnome Desktop Network Configuration
/usr/bin/gnome-network-preferences (RH 9.0 - FC-3)
Proxy configuration. Choose one of three options:- Direct internet connection
- Manual proxy configuration (specify proxy and port)
- Automatic proxy configuration (give URL)
Computers may be assigned a static IP address or assigned one dynamically. Typically a server will require a static IP while a workstation will use DHCP (dynamic IP assignment). The Linux server requires a static IP so that those who wish to use its resources can find the system consitently. It is more easily found if the IP address does not change and is static. This is not important for the Linux client workstation and thus it is easier to use an automated Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for IP address assignment.
Static IP address assignment:
Choose one of the following methods:
- Command Line: There are two commands which can assign an IP address, ip (current practice) and ifconfig (current and legacy).
- ip command:
/sbin/ip link # show list of network interfaces /sbin/ip addr add 192.168.10.12/255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.10.255 dev eth0 /sbin/ip addr show
[Potential Pitfall]: Avoid the following error by executing the command as root or use sudo:RTNETLINK answers: Operation not permitted - ifconfig command:
/sbin/ifconfig -a # show list of network interfaces even if down /sbin/ifconfig eth0 192.168.10.12 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.10.255 /sbin/ifconfig # no arguments defaults to showing the current IP configuration
[Potential Pitfall]: Avoid the following error by executing the command as root or use sudo:SIOCSIFADDR: Operation not permitted SIOCSIFFLAGS: Operation not permitted SIOCSIFNETMASK: Operation not permitted SIOCSIFBRDADDR: Operation not permitted SIOCSIFFLAGS: Operation not permitted
Broadcast address by convention would be the highest: 192.168.10.255
The gateway router can be anything, but following convention: 192.168.10.1Note: the highest and lowest addresses are based on the netmask. The previous example is based on a netmask of 255.255.255.0
- ip command:
- Red Hat / Fedora GUI tools:
- /usr/bin/neat Gnome GUI network administration tool. Handles all interfaces. Configure for Static IP or DHCP client.
(First available with Red Hat 7.2.) - /usr/bin/netcfg (Handles all interfaces) (last available in Red Hat 7.1)
- /usr/bin/neat Gnome GUI network administration tool. Handles all interfaces. Configure for Static IP or DHCP client.
- Red Hat / Fedora Console tools:
- /usr/sbin/system-config-network-tui (Text User Interface)
- /usr/sbin/netconfig (Only seems to work for the first network interface eth0 but not eth1,...)
- Directly edit configuration files/scripts. See format below.
The ip and ifconfig commands do NOT store this configuration permanently. Upon reboot this information is lost. Manually add the network configuration to the system configuration files to have them persist:
- Red Hat/Fedora/CentOS: /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 for the first NIC, ifcfg-eth1 for the second, etc
- Ubuntu/Debian: /etc/network/interfaces as shown below.
Any other commands you may want to add to the system boot sequence can be added to the end of the file /etc/rc.d/rc.local
The commands netcfg and netconfig make permanent changes to system network configuration files located in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/, so that this information is retained and used upon system boot.
The IANA has allocated IP addresses in the range of 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 for private networks.
[Potential Pitfall]: You assign an IP address and the network connection still does not work?
- Your system settings may not be compatible with your router configuration
- You still may need to add a route (see Route configuration below)
- Firewall rules may be blocking network traffic. Test by flushing all firewall rules: iptables -F
- Your system or your network may not be configured to use your upstream network
Helpful tools:
- Network Calculators: Subnet mask calculator, node calculator, mask inverter, ...
- IP subnet calculator
ip [ OPTIONS ] OBJECT COMMAND
or
ip OBJECT COMMAND
- OPTIONS: -V[ersion] | -h[uman-readable] | -s[tatistics] | -r[esolve] | -f[amily] { inet | inet6 | ipx | dnet | link } | -o[neline] | -n[etns] name | -a[ll] | -c[olor]
- OBJECT: link | addr(ess) | addrlabel | route | rule | neigh | ntable | tunnel | tuntap | maddress | mroute | mrule | monitor | xfrm | netns | l2tp | tcp_metrics
- COMMAND: add | delete | set | show | list | help
(Note: not all "OBJECT"s support all "COMMAND"s. Use the command line help. eg: ip addr help)
| OBJECT | Description |
|---|---|
| address addr a | protocol (IP or IPv6) address on a device |
| addrlabel addrl | Label configuration for protocol address selection |
| l2tp | tunnel ethernet over IP (L2TPv3) |
| link l | network device |
| maddress | multicast address |
| monitor | watch for netlink messages |
| mroute | multicast routing cache entry |
| mrule | rule in multicast routing policy database |
| neighbour neigh n | ARP or NDISC cache entry |
| netns | manage network namespaces |
| ntable | manage the neighbor cache's operation |
| route r | routing table entry |
| rule | rule in routing policy database |
| tcp_metrics tcpmetrics | manage TCP Metrics |
| tunnel | tunnel over IP |
| tuntap | manage TUN/TAP devices |
| xfrm | manage IPSec policies |
Examples:
- Assign a broadcast address: ip addr add broadcast 192.168.10.255 dev eth0
- Delete the IP address assignment from a network interface: ip addr del 192.168.10.12/24 dev eth0
- Assign an IP address using CIRD notation: ip addr add 192.168.10.12/24 broadcast 192.168.10.255 dev eth0
- Turn off/shut down a network interface: ip link set dev eth1 down
- Turn on a network interface: ip link set dev eth1 up
ifconfig interface [aftype] options | address ...
where:- interface: eth0, eth1, eth2 represent the computer ethernet interfaces
- aftype: inet (TCP/IP, default), inet6 (IPv6), ax25 (AMPR Packet Radio), ddp (Appletalk Phase 2), ipx (Novell IPX) or netrom (AMPR Packet radio)
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| up | Activate the interface. Implied if IP addresses are specified. |
| down | Shut down interface |
| arp | Enable ARP protocol on this interface. Allow ARP to detect the addresses of computer hosts attached to the network. |
| -arp | Disable ARP protocol on this interface |
| promisc | Enable promiscuous mode. Receive all packets on the network not just those destined for this interface. |
| -promisc | Disable promiscuous mode. |
| mtu ## | Specify the Maximum Transfer Unit (MTU) of the interface. The MTU is the maximum number of octets the interface is able to handle in a single transaction. Defaults: Ethernet: 1500 SLIP: 296 |
| broadcast XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX | Set the network broadcast address for this interface. |
| netmask XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX | Set the IP network mask for this interface. |
File: /etc/network/interfaces
Static IP example:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 208.88.34.106
netmask 255.255.255.248
broadcast 208.88.34.111
network 208.88.34.104
gateway 208.88.34.110
Dynamic IP (DHCP) example:
auto lo iface lo inet loopback auto eth0 iface eth0 inet dhcp auto eth1 iface eth1 inet dhcp auto eth2 iface eth2 inet dhcp auto ath0 iface ath0 inet dhcp auto wlan0 iface wlan0 inet dhcpInterfaces:
- lo: Loopback interface (network within your system without slowing down for the real ethernet based network)
- eth0: First ethernet interface card
- wlan0: First wireless network interface
Also see "man interfaces"
Ubuntu GUI Network Tools:
- /usr/bin/gnome-nettool (apt-get install gnome-nettool)
- /usr/bin/network-admin (apt-get install gnome-network-admin)
The Red Hat configuration tools store the configuration information in the file
/etc/sysconfig/network.
They will also allow one to configure routing information.
- File: /etc/sysconfig/network
Static IP address Configuration: (Configure gateway address)
NETWORKING=yes HOSTNAME=my-hostname - Hostname is defined here and by command hostname FORWARD_IPV4=true - True for NAT firewall gateways and linux routers. False for everyone else - desktops and servers. GATEWAY="XXX.XXX.XXX.YYY" - Used if your network is connected to another network or the internet. Static IP configuration. Gateway not defined here for DHCP client.OR for DHCP client configuration:NETWORKING=yes HOSTNAME=my-hostname - Hostname is defined here and by command hostname(Gateway is assigned by DHCP server.)
OR for NIS client configuration:NETWORKING=yes HOSTNAME=my-hostname - Hostname is defined here and by command hostname NISDOMAIN=NISProject1 - NIS domain to attach
- File (Red Hat/Fedora): /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
(S.u.s.e.: /etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-eth-id-XX:XX:XX:XX:XX)
This file used by the command scripts ifup and ifdownStatic IP address configuration:
DEVICE=eth0 BOOTPROTO=static BROADCAST=XXX.XXX.XXX.255 IPADDR=XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX NETMASK=255.255.255.0 NETWORK=XXX.XXX.XXX.0 ONBOOT=yes - Will activate upon system boot
RHEL/Fedora additions:- TYPE=Ethernet
- HWADDR=XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
- GATEWAY=XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
OR for DHCP client configuration:
DEVICE=eth0 ONBOOT=yes BOOTPROTO=dhcp
RHEL/Fedora additions:- IPV6INIT=no
- USERCTL=no
- PEERDNS=yes
- TYPE=Ethernet
- HWADDR=XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
To disable DHCP change BOOTPROTO=dhcp to BOOTPROTO=none
In order for updated information in any of these files to take effect, one must issue the command: service network restart (or: /etc/init.d/network restart)
The Linux OS manages outbound and inbound IP (Internet Protocol) traffic. Inbound traffic is captured based on ARP and IP address configuration. Outbound traffic is managed by routes. Routing determines the path these packets take so that they are sent to their destinations. This is required for all IP traffic, local and remote, including when multiple network interfaces are available. Routes are held by the kernel routing table.
Direct routing table entries occur when the source and destination hosts are on the same physical network and packets are sent directly from the source to the destination.
Indirect routing table entries occur when the source and destination hosts are on different physical networks. The destination host must be reached through one or more IP gateways. The first gateway is the only one which is known by the host system.
Default routing defines a gateway to use when the direct network route and the indirect host routes are not defined for a given IP address.
Static routes: IP uses a routing table to determine where packets should be sent. First the packet is examined to see if its' destination is for the local or remote network. If it is to be sent to a remote network, the routing table is consulted to determine the path. If there is no information in the routing table then the packet is sent to the default gateway. Static routes are set with the route command and with the configuration file:
- Red Hat/Fedora: /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-eth0
- Red Hat 7: /etc/sysconfig/static-routes
- S.u.s.e. 9.2: /etc/sysconfig/network/routes
10.2.3.0/16 via 192.168.10.254See command: /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifup-routes eth0
Dynamic routes: RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is used to define dynamic routes. If multiple routes are possible, RIP will choose the shortest route. (Fewest hops between routers not physical distance.) Routers use RIP to broadcast the routing table over UDP port 520. The routers would then add new or improved routes to their routing tables.
Man pages:
- route - show / manipulate the IP routing table (Static route)
Show routes:
Manipulate routes:Option Description -n display IP addresses. Do not resolve host names for faster results. -e Print more extensive information about routes. -v Verbose. --help Route command information.
Examples:Option Description add or del or neither Add or delete route information. If not specified then print route table information. -host XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX Add a single computer host identified by the IP address. -net XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX Add a network identified by the network address, to the route. gw XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX Specify the network gateway. netmask XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX Specify the network netmask. default Of all the routes specified, identify one as the default network route.
(typically the gateway is specified as the default route)- Show routing table: route -e
- Access individual computer host specified via network interface card eth1:
route add -host 123.213.221.231 eth1 - Access ISP network identified by the network address and netmask using network interface card eth0:
route add -net 10.13.21.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.10.254 eth0
Conversely: route del -net 10.13.21.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.10.254 eth0 - Specify default gateway to use to access remote network via network interface card eth0:
route add default gw 201.51.31.1 eth0
(Gateway can also be defined in /etc/sysconfig/network) - Specify two gateways for two network destinations:
(i.e. one external, one internal private network. Two routers/gateways
will be specified.)
Add internet gateway as before: route add default gw 201.51.31.1 eth0
Add second private network: route add -net 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.0.0.0 gw 192.168.10.254 eth0
- ip - show / manipulate routing, devices, policy routing and tunnels
Examples:- Show routing table: ip route
- Add a new route: ip route add 192.168.10.0/24 via 192.168.10.1
(where the network address is 192.168.10.0, the netmask is "/24" or 255.255.255.0 and the router has the IP address 192.168.10.1) - Specify default gateway to use to access remote network via network interface card eth0: ip route add default 192.168.10.0/24 via 192.168.10.1
- Delete a route: ip route del 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0
- Delete a default route: ip route del default
- fuser - identify processes using files or sockets
Show which processes are using a particular file/directory: fuser file-name
This command will list the process ID and a descriptor indicating the following:- c: Durrent directory
- e: Executable
- f: a file open for reading
- F: a file open for writing
- r: Roo directory
- m: Memory Mapped File/Directory
List processes using a specified TCP/UDP socket: fuser -v -n tcp 8080
Kill a process using a specified TCP/UDP socket: fuser -i -k 8080/tcp
Any signal can be sent to the process, not just "KILL". (fuser -l): HUP QUIT TRAP ABRT IOT STOP etc
Routers and Routing:
Routing software can be run on Linux so that it will act as a router. Older packages such as routed and gated are no longer supported. Quagga, a fork of GNU "Zebra", has replaced them. Quagga is a routing software suite, providing implementations of OSPFv2, OSPFv3, RIP v1 and v2, RIPng and BGP-4 for Linux platforms.
Installation: RH/CentOS: yum install quagga
Quagga Man Pages:- zebra - a routing manager for use with associated Quagga components
- bgpd - a BGPv4, BGPv4+, BGPv4- routing engine for use with Quagga routing software
- isisd - an IS-IS routing engine for use with Quagga routing software
- ospfd - an OSPFv2 routing engine for use with Quagga routing software
- ospf6d - an OSPFv3 routing engine for use with Quagga routing software
- ripd - a RIP routing engine for use with Quagga routing software
- ripngd - a RIPNG routing engine for use with Quagga routing software
- vtysh - a integrated shell for Quagga routing software
Assign more than one IP address to one ethernet card:
ifconfig eth0 XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast XXX.XXX.XXX.255 ifconfig eth0:0 192.168.10.12 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.10.255 ifconfig eth0:1 192.168.10.14 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.10.255 route add -host XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX dev eth0 route add -host 192.168.10.12 dev eth0 route add -host 192.168.10.14 dev eth0In this example 0 and 1 are aliases in addition to the regular eth0. The result of the ifconfig command:
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:10:4C:25:7A:3F
inet addr:XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX Bcast:XXX.XXX.XXX.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:14218 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:1362 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:1 txqueuelen:100
Interrupt:5 Base address:0xe400
eth0:0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:10:4C:25:7A:3F
inet addr:192.168.10.12 Bcast:192.168.10.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
Interrupt:5 Base address:0xe400
eth0:1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:10:4C:25:7A:3F
inet addr:192.168.10.14 Bcast:192.168.10.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
Interrupt:5 Base address:0xe400
Config file: /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0:0
DEVICE=eth0:0 ONBOOT=yes BOOTPROTO=static BROADCAST=192.168.10.255 IPADDR=192.168.10.12 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 NETWORK=192.168.10.0 ONBOOT=yes
Aliases can also be shut down independently. i.e.: ifdown eth0:0
The option during kernel compile is: CONFIG_IP_ALIAS=y (Enabled by default in Redhat)
Note: The Apache web server can be configured so that different IP addresses can be assigned to specific domains being hosted. See Apache configuration and "configuring an IP based virtual host" in the YoLinux Web site configuration tutorial.
DHCP Linux Client: get connection info: /sbin/pump -i eth0 --status
(Red Hat Linux 7.1 and older)
Device eth0 IP: 4.XXX.XXX.XXX Netmask: 255.255.252.0 Broadcast: 4.XXX.XXX.255 Network: 4.XXX.XXX.0 server 131.XXX.XXX.4 Next server 0.0.0.0 Gateway: 4.XXX.XXX.1 Domain: vz.dsl.genuity.net Nameservers: 4.XXX.XXX.1 4.XXX.XXX.2 4.XXX.XXX.3 Renewal time: Sat Aug 11 08:28:55 2001 Expiration time: Sat Aug 11 11:28:55 2001
This is a three step process:
- Issue the command: hostname new-host-name
- Change network configuration file: /etc/sysconfig/network
Edit entry: HOSTNAME=new-host-name - Restart systems which relied on the hostname (or reboot):
- Restart network services: service network restart
(or: /etc/init.d/network restart) - Restart desktop:
- Bring down system to console mode: init 3
- Bring up X-Windows: init 5
- Restart network services: service network restart
The hostname may be changed at runtime using the command: sysctl -w kernel.hostname="superserver"
Note that hostnames may only contain alphanumeric characters, minus signs ("-"), and periods ("."). They must begin with an alphabetic character and end with an alphanumeric character.
Change the host name using GUI tool: /usr/sbin/system-config-network
(Red Hat / Fedora / CentOS)
Hostname entries are made in two places:
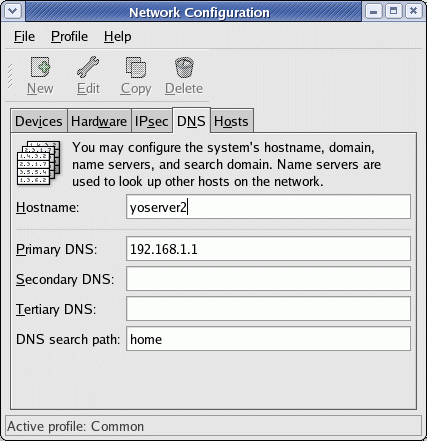
Select the "DNS" tab.
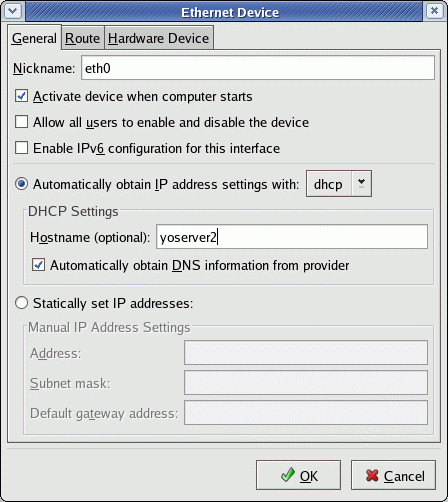
Select the "Devices" tab + "Edit" + the "General" tab.
Commands for starting and stopping TCP/IP network services on a Network Interface Card (NIC):
- Activate: /sbin/ifup eth0
(Also: ifconfig eth0 up - Note: Even if no IP address is assigned you can listen.) - De-Activate: /sbin/ifdown eth0
(Also: ifconfig eth0 down)
files in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
GUI Interface control/configuration:
- Start/Stop network interfaces
/usr/bin/system-control-network (Fedora Core 2/3)
/usr/bin/redhat-control-network (RH 9.0 - FC-1) - Configure Ethernet, ISDN, modem, token Ring, Wireless or DSL network connection:
/usr/sbin/system-config-network-druid (FC2/3)
/usr/sbin/redhat-config-network-druid (RH 9 - FC-1)
Subnetting is a methodology used to divide a network into multiple logical networks (subnets). Subnets are often defined for geographical or location reasons. Subnet masks are defined to reflect the number of computer systems and the IP addresses of the systems on the subnet.
| M A S K |
# OF SUB NETS |
Slash Fmt |
CLASS A HOSTS |
CLASS A MASK |
CLASS B HOSTS |
CLASS B MASK |
CLASS C HOSTS |
CLASS C MASK |
CLASS C SUB HOSTS |
CLASS C SUB MASK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 255 | 1 or 256 |
/32 | 16,777,214 | 255.0.0.0 | 65,534 | 255.255.0.0 | 254 | 255.255.255.0 | Invalid 1 address |
255.255.255.255 |
| 254 | 128 | /31 | 33,554,430 | 254.0.0.0 | 131,070 | 255.254.0.0 | 510 | 255.255.254.0 | Invalid 2 addresses |
255.255.255.254 |
| 252 | 64 | /30 | 67,108,862 | 252.0.0.0 | 262,142 | 255.252.0.0 | 1,022 | 255.255.252.0 | 2 hosts 4 addresses |
255.255.255.252 |
| 248 | 32 | /29 | 134,217,726 | 248.0.0.0 | 524,286 | 255.248.0.0 | 2,046 | 255.255.248.0 | 6 hosts 8 addresses |
255.255.255.248 |
| 240 | 16 | /28 | 268,435,454 | 240.0.0.0 | 1,048,574 | 255.240.0.0 | 4,094 | 255.255.240.0 | 14 hosts 16 addresses |
255.255.255.240 |
| 224 | 8 | /27 | 536,870,910 | 224.0.0.0 | 2,097,150 | 255.224.0.0 | 8,190 | 255.255.224.0 | 30 hosts 32 addresses |
255.255.255.224 |
| 192 | 4 | /26 | 1,073,741,822 | 192.0.0.0 | 4,194,302 | 255.192.0.0 | 16,382 | 255.255.192.0 | 62 hosts 64 addresses |
255.255.255.192 |
| 128 | 2 | /25 | 2,147,483,646 | 128.0.0.0 | 8,388,606 | 255.128.0.0 | 32,766 | 255.255.128.0 | 126 hosts 128 addresses |
255.255.255.128 |
| Binary position | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Value | 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| Example: 192 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Example 192=128+64
Some addresses are reserved and outside this scope. Loopback (127.0.0.1), reserved class C 192.168.XXX.XXX, reserved class B 172.31.XXX.XXX and reserved class A 10.XXX.XXX.XXX.
Subnet Example:
Your ISP assigns you a subnet mask of 255.255.255.248 for your office.- 208.88.34.104 Network Base address
- 208.88.34.105 Computer 1
- 208.88.34.106 Computer 2
- 208.88.34.107 Computer 3
- 208.88.34.108 Computer 4
- 208.88.34.109 Computer 5
- 208.88.34.110 DSL router/Gateway
- 208.88.34.111 Broadcast address
Links:
- Subnet calculator
- IPV4 subnet calculator - IPV6 subnet calculator
- IP Subnetting, Variable Subnetting, and CIDR (Supernetting)
The concept of network classes is a little obsolete as subnets are now used to define smaller networks using CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) as detailed above. These subnets may be part of a class A, B, C, etc network. For historical reference the network classes are defined as follows:
- Class A: Defined by the first 8 bits with a range of 0 - 127.
First number (8 bits) is defined by Internic i.e. 77.XXX.XXX.XXX
One class A network can define 16,777,214 hosts.
Range: 0.0.0.0 - 127.255.255.255 - Class B: Defined by the first 8 bits with a range from 128 - 191
First two numbers (16 bits) are defined by Internic i.e. 182.56.XXX.XXX
One class B network can define 65,534 hosts.
Range: 128.0.0.0 - 191.255.255.255 - Class C: Defined by the first 8 bits with a range from 192 - 223
First three numbers (24 bits) are defined by Internic i.e. 220.56.222.XXX
One class B network can define 254 hosts.
Range: 192.0.0.0 - 223.255.255.255 - Class D: Defined by the first 8 bits with a range from 224 - 239
This is reserved for multicast networks (RFC988)
Range: 224.0.0.0 - 239.255.255.255 - Class E: Defined by the first 8 bits with a range from 240 - 255
This is reserved for experimental use.
Range: 240.0.0.0 - 247.255.255.255
Forwarding allows the network packets on one network interface (i.e. eth0) to be forwarded to another network interface (i.e. eth1). This will allow the Linux computer to connect ("ethernet bridge") or route network traffic.
The bridge configuration will merge two (or several) networks into one single network topology. IpTables firewall rules can be used to filter traffic.
A router configuration can support multicast and basic IP routing using the "route" command. IP masquerading (NAT) can be used to connect private local area networks (LAN) to the internet or load balance servers.
- Turn on IP forwarding to allow Linux computer to act as a gateway or router.
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Default is 0. One can add firewall rules by using iptables (or ipchains).Another method is to alter the Linux kernel config file: /etc/sysctl.conf Set the following value:
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
See file /etc/sysconfig/network for storing this configuration.
FORWARD_IPV4=true
Change the default "false" to "true".
All methods will result in a proc file value of "1". Test: cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
The TCP Man page - Linux Programmer's Manual and /usr/src/linux/Documentation/proc.txt (Kernel 2.2 RH 7.0-) cover /proc/sys/net/ipv4/* file descriptions.
Also see: (YoLinux tutorials)
- Configure Linux as an internet gateway router: Using Linux and iptables/ipchains to set up an internet gateway for home or office (iptables)
- Load balancing servers using LVS (Linux Virtual Server) (ipvsadm)
Manual method: This does not alter the permanent configuration and will only configure support until the next reboot.
- cd /lib/modules/2.2.5-15/net/ - Use kernel version for your system. This example uses 2.2.5-15
(Fedora Core 3: /lib/modules/2.6.12-1.1381_FC3/kernel/net/)
Here you will find the modules supported by your system.
It can be permanently added to:- /etc/modprobe.conf (kernel 2.6)
- /etc/modules.conf (kernel 2.4)
- (or for older systems: /etc/conf.modules)
alias eth0 3c59x
- /sbin/insmod 3c59x (For a 3Com ethernet card)
This inserts the specified module into the kernel. - /sbin/modprobe 3c59x
This also loads a module into the system kernel.
Modprobe command line options:- -r : to unload the module.
- /sbin/modprobe -l \* : list all modules.
- /sbin/modprobe -lt net \* : List only network modules
- /sbin/modprobe -t net \* : Try loading all network modules and see what sticks. (act of desperation)
- ifconfig ...
The easy way: Red Hat versions 6.2 and later, ship with Kudzu, a device detection program which runs during system initialization. (/etc/rc.d/init.d/kudzu) This can detect a newly installed NIC and load the appropriate driver. Then use /usr/sbin/netconfig to configure the IP address and network settings. The configuration will be stored so that it will be utilized upon system boot.
Systems with two NIC cards: Typically two cards are used when connecting to two networks. In this case the device must be defined using one of three methods:
- Use the Red Hat GUI tool /usr/bin/netcfg
OR
- Define network parameters in configuration files:
Define new device in file (Red Hat/Fedora) /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
(S.u.s.e 9.2: /etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-eth-id-XX:XX:XX:XX:XX)DEVICE=eth1 BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR=192.168.10.12 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX HOSTNAME=node-name.name-of-domain.com DOMAIN=name-of-domain.comSpecial routing information may be specified, if necessary, in the file
(Red Hat/Fedora): /etc/sysconfig/static-routes
(S.u.s.e. 9.2: /etc/sysconfig/network/routes)Example:
eth1 net XXX.XXX.XXX.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw XXX.XXX.XXX.XXXOR
- Define network parameters using Unix command line interface:
Define IP address:
ifconfig eth0 XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast XXX.XXX.XXX.255
ifconfig eth1 192.168.10.12 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.10.255
If necessary, define route with with the route command:
Examples:route add default gw XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX dev eth0 route add -net XXX.XXX.XXX.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX dev eth0Where XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX is the gateway to the internet as defined by your ISP or network operator.If a mistake is made just repeat the route command substituting "del" in place of "add".
This is usually not necessary because most ethernet adapters can auto-negotiate link speed and duplex setting.
- List NIC speed and configuration: mii-tool
eth0: negotiated 100baseTx-FD flow-control, link okVerbose mode: mii-tool -v
eth0: negotiated 100baseTx-FD flow-control, link ok product info: Intel 82555 rev 4 basic mode: autonegotiation enabled basic status: autonegotiation complete, link ok capabilities: 100baseTx-FD 100baseTx-HD 10baseT-FD 10baseT-HD advertising: 100baseTx-FD 100baseTx-HD 10baseT-FD 10baseT-HD flow-control link partner: 100baseTx-FD 100baseTx-HD 10baseT-FD 10baseT-HD flow-control - Set NIC configuration: mii-tool -F option
Option Parameters -F 100baseTx-FD
100baseTx-HD
10baseT-FD
10baseT-HD-A 100baseT4
100baseTx-FD
100baseTx-HD
10baseT-FD
10baseT-HD
Man Pages:
- mii-tool - view, manipulate media-independent interface status
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ethtool -g eth0 | Queries ethernet device for rx/tx ring parameter information. |
| ethtool -a eth0 | Queries ethernet device for pause parameter information. |
| ethtool -c eth0 | Queries ethernet device for coalescing information. |
| ethtool -i eth0 | Queries ethernet device for associated driver information. |
| ethtool -d eth0 | Prints a register dump for the specified ethernet device. |
| ethtool -k eth0 | Queries ethernet device for offload information. |
| ethtool -S eth0 | Queries ethernet device for NIC and driver statistics. |
| ethtool -p eth0 | This command is used to identify the ethernet hardware port associated with the device specified by blinking the LED on the port. |
Man Pages:
- ethtool - Display or change ethernet card settings
- Commercial VPN Linux software solutions - YoLinux
- OpenSWAN.org - IPSec VPN for Linux
- strongSwan.org - IPSec VPN for Linux (follow-on to FreeSWAN)
- FreeSWAN tutorial - howto
- OpenVPN - SSL VPN solution for site to site, WiFi security, and enterprise-scale remote access with load balancing, failover, and fine-grained access-controls.
- SSL-Explorer - Java SLL based VPN
- Quagga dynamic routing suite VLAN
- NTopng traffic analysis
- CIPE: Crypto IP Encapsulation (Easiest way to configure two
Linux gateways connecting two private networks over the internet with
encryption.)
- CIPE Home page - CIPE is a simple encapsulation system that securely connects two subnets.
- VPN HowTo - Matthew D. Wilson
- PPTP: Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol - virtual private networks
- /etc/rc.d/init.d/network start - command to start, restart or stop the network
- netstat - Display connections, routing tables, stats etc
- List externally connected processes: netstat -punta
- -a: Show both listening and non-listening sockets.
- -p: Show PID of process owning socket
- -u: Show UDP
- -t: Show TCP
- -n: Show IP addresses only. Don't resolve host names
- -g: Show multi-cast group membership info
- -c: Continuous mode - update info every second
- -v: Verbose
- -e: Extended information
- -o: show network timer information
- List all connected processes: netstat -nap
- List all processes with a TCP connection: netstat -tlnp
This will list open TCP ports:- -t: TCP
- -l: listening ports only
- -n: no host name lookup
- -p: process ID
- Show network statistics: netstat -s
- Display routing table info: netstat -rn
$ netstat -nr Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0Flags:- G: route uses gateway
- U: Interface is "up"
- H: Only a single host is accessible (eg. loopback)
- D: Entry generated by ICMP redirect message
- M: Modified by ICMP redirect message
- Display processes connecting with ssh (port 22): netstat -aon | grep ':22 '
$ netstat -aon | grep :22 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN off (0.00/0/0) tcp 0 36 172.131.56.120:22 118.57.17.204:37951 ESTABLISHED on (0.24/0/0) tcp 0 0 172.131.56.120:22 116.31.114.52:46438 ESTABLISHED keepalive (7160.36/0/0) tcp 0 0 172.131.56.120:22 116.31.114.52:64874 ESTABLISHED keepalive (7209.52/0/0) tcp 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN off (0.00/0/0)- -a: Show both listening and non-listening sockets.
- -o: show network timer information
- -n: no host name lookup
- Display interface statistics: netstat -i
$ netstat -i Kernel Interface table Iface MTU Met RX-OK RX-ERR RX-DRP RX-OVR TX-OK TX-ERR TX-DRP TX-OVR Flg eth0 1500 0 2224 0 0 0 1969 0 0 0 BMRU lo 16436 0 1428 0 0 0 1428 0 0 0 LRUWhere:- RX-OK/TX-OK: number of packets transmitted/received error free
- RX-ERR/TX-ERR: number of damaged/error packets transmitted/received
- RX-DRP/TX-DRP: number of dropped packets
- RX-OVR/TX-OVR: number of packets dropped because of a buffer overrun
- B: A broadcast address has been set
- L: This interface is a loopback device
- M: All packets are received
- N: Trailers are avoided
- O: ARP is turned off for this interface
- P: Point-to-point connection
- R: Interface is running
- U: Interface is up
- List externally connected processes: netstat -punta
- rtstat/lnstat - unified linux network statistics
(reports contents of /proc/net/stat/ and routing cache statistics) - nstat/rtacct - network statistics tools
(monitor kernel snmp counters and network interface statistics) - ping - send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST packets to network hosts. Use Cntl-C to stop ping.
- traceroute - print the route packets take to network host.
(Ubuntu Note: Typically Ubuntu installs tracepath for IPv4 and traceroute6 for IPv6. One can install traceroute: apt-get install traceroute)- traceroute IP-address-of-server
- traceroute domain-name-of-server
- mtr
- a network diagnostic tool introduced in Fedora - Like traceroute
except it gives more network quality and network diagnostic info. Leave
running to get real time stats. Reports best and worst round trip times
in milliseconds.
- mtr IP-address-of-server
- mtr domain-name-of-server
Example: mtr --report www.yahoo.com[prompt]$ mtr --report www.yahoo.com Start: Sun May 22 19:26:58 2016 HOST: mydesktop Loss% Snt Last Avg Best Wrst StDev 1.|-- Wireless_Broadband_Router 0.0% 10 0.4 0.4 0.3 0.4 0.0 2.|-- 61.218.111.1 0.0% 10 4.3 5.4 3.2 9.4 1.9 3.|-- 142.202.104.222 0.0% 10 6.7 7.5 6.1 9.9 0.9 4.|-- ae8---0.scr02.lsan.ca.fro 0.0% 10 6.1 7.1 6.1 8.2 0.6 5.|-- ae1---0.cbr01.lsan.ca.fro 0.0% 10 7.4 7.7 5.7 16.6 3.1 6.|-- lag-101.ear2.LosAngeles1. 80.0% 10 6.0 9.5 6.0 13.0 4.9 7.|-- ae-1-51.ear3.Seattle1.Lev 90.0% 10 32.4 32.4 32.4 32.4 0.0 8.|-- YAHOO-INC.ear3.Seattle1.L 0.0% 10 34.2 33.1 31.7 35.1 0.9 9.|-- ae-7.pat1.gqb.yahoo.com 0.0% 10 36.7 35.9 35.1 36.9 0.3 10.|-- et-1-0-0.msr2.gq1.yahoo.c 0.0% 10 37.5 39.3 36.6 57.1 6.2 11.|-- et-1-0-0.clr1-a-gdc.gq1.y 0.0% 10 37.2 49.1 37.2 119.3 26.0 12.|-- et-18-1.fab7-1-gdc.gq1.ya 0.0% 10 38.5 38.1 36.9 39.9 0.7 13.|-- po-15.bas1-7-prd.gq1.yaho 0.0% 10 38.0 37.4 36.6 38.5 0.0 14.|-- ir1.fp.vip.gq1.yahoo.com 0.0% 10 40.5 37.9 36.7 40.5 1.1
- whois - Lookup a domain name in the internic whois database.
- finger - Display information on a system user. i.e. finger user@host Uses $HOME/.plan and $HOME/.project user files.
- iptables - IP firewall administration (Linux kernel 2.6/2.4) See YoLinux firewall/gateway configuration.
- ipchains - IP firewall administration (older Linux kernel 2.2) See YoLinux firewall/gateway configuration.
- host - Give a host name and the command will return IP address. Unlike nslookup, the host command will use both /etc/hosts as well as DNS.
Example: host domain-name-of-server - nslookup - Give a host name and the command will return IP address. Also see Testing your DNS (YoLinux Tutorial) Note that nslookup does not use the /etc/hosts file.
The network listening daemons listen and respond to all network socket connections made on the TCP/IP ports assigned to it. The ports are defined by the file /etc/services. When a connection is made, the listener will attempt to invoke the assigned program and pipe the data to it. This simplified matters by allowing the assigned program to read from stdin instead of making its own sockets connection. The listener handles the network socket connection. Two network listening and management daemons have been used in Red Hat Linux distributions:
- inetd: Red Hat 6.x and older
- xinetd: Red Hat 7.0-9.0, RHEL 5-8, Fedora
Configuration file: /etc/inetd.conf
Entries in this file consist of a single line made up of the following fields:
service socket-type protocol wait user server cmdline
- service: The name assigned to the service. Matches the name given in the file /etc/services
- socket-type:
- stream: connection protocols (TCP)
- dgram: datagram protocols (UDP)
- raw
- rdm
- seqpacket
- protocol: Transport protocol name which matches a name in the file /etc/protocols. i.e. udp, icmp, tcp, rpc/udp, rpc/tcp, ip, ipv6
- wait: Applies only to datagram protocols (UDP).
- wait[.max]: One server for the specified port at any time (RPC)
- nowait[.max]: Continue to listen and launch new services if a new connection is made. (multi-threaded)
- user[.group]: login id of the user the process is executed under. Often nobody, root or a special restricted id for that service.
- server: Full path name of the server program to be executed.
- cmdline: Command line to be passed to the server. This includes argument 0 (argv[0]), that is the command name. This field is empty for internal services. Example of internal TCP services: echo, discard, chargen (character generator), daytime (human readable time), and time (machine readable time). (see RFC)
Sample File: /etc/inetd.conf
#echo stream tcp nowait root internal
#echo dgram udp wait root internal
ftp stream tcp nowait root /usr/sbin/tcpd in.ftpd -l -a
#pop-3 stream tcp nowait root /usr/sbin/tcpd ipop3d
#swat stream tcp nowait.400 root /usr/sbin/swat swat
A line may be commented out by using a '#' as the first character in the line.
This will turn the service off.
The maximum length of a line is 1022 characters.
The inet daemon must be restarted to pick up
the changes made to the file:
/etc/rc.d/init.d/inetd restart
For more information see the man pages "inetd" and "inetd.conf".
Xinetd has access control mechanisms, logging capabilities, the ability to make services available based on time, and can place limits on the number of servers that can be started, redirect services to different ports and network interfaces (NIC) or even to a different server, chroot a service etc... and thus a worthy upgrade from inetd.
Use the command chkconfig --list to view all system services and their state. It will also list all network services controlled by xinetd and their respective state under the title "xinetd based services". (Works for xinetd (RH7.0+) but not inetd)
The xinetd network daemon uses PAM also called network wrappers which invoke the /etc/hosts.allow and /etc/hosts.deny files.
Configuration file: /etc/xinetd.conf which in turn uses configuration files found in the directory /etc/xinetd.d/.
To turn a network service on or off:
- Edit the file /etc/xinetd.d/service-name
Set the disable value:
disable = yes
or
disable = no Restart the xinetd process using the signal:- SIGUSR1 (kill -SIGUSR1 process-id) - Soft reconfiguration does not terminate existing connections. (Important if you are connected remotely)
- SIGUSR2 - Hard reconfiguration stops and restarts the xinetd process.
OR
- Use the chkconfig command: chkconfig service-name on
(or off)
This command will also restart the xinetd process to pick up the new configuration.
The file contains entries of the form:
service service-name
{
attribute assignment-operator value value ...
...
{
Where:
- attribute:
- disable:
- yes
- no
- type:
- RPC
- INTERNAL:
- UNLISTED: Not found in /etc/rpc or /etc/services
- id: By default the service id is the same as the service name.
- socket_type:
- stream: TCP
- dgram: UDP
- raw: Direct IP access
- seqpacket: service that requires reliable sequential datagram transmission
- flags: Combination of: REUSE, INTERCEPT, NORETRY, IDONLY, NAMEINARGS, NODELAY, DISABLE, KEEPALIVE, NOLIBWRAP.
See the xinetd man page for details. - protocol: Transport protocol name which matches a name in the file /etc/protocols.
- wait:
- no: multi-threaded
- yes: single-threaded - One server for the specified port at any time (RPC)
- user: See file : /etc/passwd
- group: See file : /etc/group
- server: Program to execute and receive data stream from socket. (Fully qualified name - full path name of program)
- server_args: Unlike inetd, arg[0] or the name of the service is not passed.
- only_from: IP address, factorized address, netmask range, hostname or network name from file /etc/networks.
- no_access: Deny from ... (inverse of only_from)
- access_times
- port: See file /etc/services
The best source of information is the man page and its many examples. - disable:
- assignment-operator:
- =
- +=: add a value to the set of values
- -=: delete a value from the set of values
Then restart the daemon: /etc/rc.d/init.d/xinetd restart
Example from man page: Limit telnet sessions to 8 Mbytes of memory and a total 20 CPU seconds for child processes.
service telnet
{
socket_type = stream
wait = no
nice = 10
user = root
server = /usr/etc/in.telnetd
rlimit_as = 8M
rlimit_cpu = 20
}
[Pitfall] Red Hat 7.1 with updates as of 07/06/2001 required that I restart the xinetd services before FTP would work properly even though xinetd had started without failure during the boot sequence. I have no explanation as to why this occurs or how to fix it other than to restart xinetd: /etc/rc.d/init.d/xinetd restart.
Man Pages:
For more info see:
- LinuxFocus.org: xinetd - Frederic Raynal
- RedHat.com: Controlling Access to Services
- GitHub: xinetd
- See RFC's: 862, 863, 864, 867, 868, 1413.
- man page xinetd, xinetd.conf, xinetd.log
Most of the original Unix remote commands have been superceded by secure shell equivalents. Instead of telnet, rsh or rlogin, one should use the encrypted connection ssh.
- telnet - user interface to the TELNET protocol
- rlogin - remote login
- rsh - remote shell to execute a command and return results
- uux - Remote command execution over UUCP
- rcp - remote file copy
- uucp - Unix to Unix copy (AWS and RHEL EPEL repo)
uuxqt - UUCP execution daemon
uucico - UUCP file transfer daemon
cu - Call up another system (cu is an old legacy command which is reported to not work very well)
The "rwho" command is used to display users logged into computers on your LAN.
By default, Red Hat Linux has the network interface to the rwhod disabled. Thus if one issues the command "rwho", you will only see who is logged into the system you are logged into and not remote systems on the network. This is a safe approach for internet servers as it reduces the exposure of a service which could be exploited by hackers. If you wish to use rwhod on a local private and firewall protected network, here is how:
Allow broadcast capabilities. Edit /etc/init.d/rwhod
change from: daemon rwhod
to: daemon rwhod -b
Start service:
- Set service to start with system boot: chkconfig --level 345 rwhod on
- Start rwhod service: service rwhod start
(or: service rwhod restart)
Man pages:
- rwho: who is logged in on local network machines
- rwhod: system status server
- who: show who is logged on to the same system
Rpcbind or portmapper are required to manage RPC (Remote Procedure Call) requests from services like NFS (file sharing services), NIS (Network Information Services) and SAMBA.
rpcbind is newer and used on RHEL 6,7 / Ubuntu 10.04, 12.04, 14.04 and later systems while portmapper was used on RHEL5 or prior systems. Rpcbind and portmapper are both server based services which manages RPC program number requests and returns universal addresses. The rpc service tells rpcbind the address on which it is listening and the RPC program numbers it will serve. Clients first contact rpcbind to lookup where its request should be sent.
An RPC server makes available a collection of procedures (programs) that a client system may call and then receive the returned results. The list of services available is listed in /etc/rpc on the server. The message communication is in a machine independent form called XDR (External Data Representation format).
- rpcbind server:
- Install service:
- RHEL6+: sudo yum install rpcbind
- Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install rpcbind
- Start service:
- /etc/init.d/rpcbind start
- service rpcbind start (Red Hat/Fedora)
- Install service:
- /etc/init.d/portmap start
- service portmap start (Red Hat/Fedora)
List RPC services supported: [root]# rpcinfo -p localhost
program vers proto port service
100000 4 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 3 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 4 udp 111 portmapper
100000 3 udp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100024 1 udp 36133 status
100024 1 tcp 47367 status
...
...
Man Pages:
- rpc - Remote Procedure Call
- rpcinfo - report RPC information
- /etc/rpc - rpc program number data base
- xdr - Remote Procedure Call
- rpcbind:
- rpcbind - port to RPC program number mapper service
- portmapper:
Pluggable Authentication Modules for Linux (TCP Wrappers)
This system allows or denies network access. One can reject or allow specific IP addresses or subnets to access your system.
File: /etc/hosts.allow
in.ftpd:208.188.34.105This specifically allows the given IP address to ftp to your system. One can also specify an entire domain. i.e. .name-of-domain.com
Note the beginning ".".
File: /etc/hosts.deny
ALL:ALLThis generally denies any access.
File: /etc/inetd.conf
ftp stream tcp nowait root /usr/sbin/tcpd in.ftpd -l -a
The inet daemon accepts the incoming network stream and assigns it to the PAM TCP wrapper, /usr/sbin/tcpd, which accepts or denies the network connection as defined by /etc/hosts.allow and /etc/hosts.deny and then passes it along to ftp. This is logged to /var/log/secure
Advanced PAM: More specific access can be assigned and controlled by controlling the level of authentication required for access.
Files reflect the inet service name. Rules and modules are stacked to achieve the level of security desired.
See the files in /etc/pam.d/... (some systems use /etc/pam.conf)
The format: service type control module-path module-arguments
- auth - (type) Password is required for the user
- nullok - Null or non-existent password is acceptable
- shadow - encrypted passwords kept in /etc/shadow
- account - (type) Verifies password. Can track and force password changes.
- password - (type) Controls password update
- retry=3 - Sets the number of login attempts
- minlen=8 - Set minimum length of password
- session - (type) Controls monitoring
Modules:
- /lib/security/pam_pwdb.so - password database module
- /lib/security/pam_shells.so -
- /lib/security/pam_cracklib.so - checks is password is crackable
- /lib/security/pam_listfile.so
After re-configuration, restart the inet daemon: killall -HUP inetd
For more info see:
ICMP is the network protocol used by the ping and traceroute commands.
ICMP redirect packets are sent from the router to the host to inform the host of a better route. To enable ICMP redirect, add the following line to /etc/sysctl.conf :
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 1
Add the following to the file: /etc/rc.d/rc.local
for f in /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/*/accept_redirects
do
echo 1 > $f
done
Command to view Kernel IP routing cache: /sbin/route -Cn
NOTE: This may leave you vulnerable to hackers as attackers may alter your routes.
The following firewall rules will drop ICMP requests.
iptables -A OUTPUT -p icmp -d 0/0 -j DROPIpchains:
ipchains -A output -p icmp -d 0/0 -j DENYOR drop all incoming pings:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/icmp_echo_ignore_allThis is sometimes necessary to look invisible to DOS (Denial Of Service) attackers who use ping to watch your machine and launch an attack when it's presence is detected
TC:
Install:- Ubuntu/Debian: apt-get install iproute
- Red Hat/CentOS/Fedora: yum install iproute
The Linux Kernel is capable of controlling bandwidth peaks, traffic prioritization and scheduling and if necessary, dropping excess traffic, all using the traffic control command "tc" to manage a set of queues (default queue: pfifo_fast).
Bandwidth control is called traffic shaping. This is often done to avoid exceeding the bandwidth when sending traffic to a particular device such as a wireless modem during peak network bursts.
Traffic prioritization includes reordering network packets so that certain traffic is guarenteed to be sent by a given time.
Packet dropping can be performed on ingress and egress packets to achieve a desired bandwidth.
Examples: limit data rate to 4 Mbps so that data rate does not exceed the capability of a wireless networking device:
- tc class add dev eth1 parent 1:0 classid 1:1 htb rate 4.0mbit prio 0
Create main class 1:1 with the assigned datarate 4 Mbit/sec - tc filter add dev eth1 parent 1:0 prio 0 protocol ip u32 match ip dst 192.168.1.20/32 match ip protocol ip 0xffff flowid 1:10
Create filter assigned to class 1:0 and 1:1
- tc - show or manipulate network traffic control settings
- tc-cbq - CBQ - Class Based Queueing - contains shaping elements as well as prioritizing capabilities.
tc qdisc ... dev dev ( parent classid | root) [ handle major: ] cbq [ allot bytes ] avpkt bytes bandwidth rate [ cell bytes ] [ ewma log ] [ mpu bytes ]
tc class ... dev dev parent major:[minor] [ classid major:minor ] cbq allot bytes [ bandwidth rate ] [ rate rate ] prio priority [ weight weight ] [ minburst packets ] [ maxburst packets ] [ ewma log ] [ cell bytes ] avpkt bytes [ mpu bytes ] [ bounded isolated ] [ split handle & defmap defmap ] [ estimator interval timeconstant ] - tc-htb - Hierarchy Token Bucket (simple replacement for CBQ)
tc qdisc ... dev dev ( parent classid | root) [ handle major: ] htb [ default minor-id ]
tc class ... dev dev parent major:[minor] [ classid major:minor ] htb rate rate [ ceil rate ] burst bytes [ cburst bytes ] [ prio priority ] - tc-drr - deficit round robin scheduler - flexible replacement for Stochastic Fairness Queuing
tc qdisc ... add drr [ quantum bytes ] - tc-sfq - Stochastic Fairness Queueing
tc qdisc ... divisor hashtablesize limit packets perturb seconds quan‐tum bytes - tc-hfsc - HFSC - Hierarchical Fair Service Curve's control
tc qdisc add ... hfsc [ default CLASSID ]
tc class add ... hfsc [ [ rt SC ] [ ls SC ] | [ sc SC ] ] [ ul SC ] - tc-choke - CHOose and KEep scheduler - classless qdisc designed to both identify and penalize flows that monopolize the queue. CHOKe is a variation of RED, and the configuration is the same as RED
tc qdisc ... choke limit bytes min bytes max bytes avpkt bytes burst packets [ ecn ] [ bandwidth rate ] probability chance - tc-red - Random Early Detection - classless qdisc to drop packets gracefully
tc qdisc ... red limit bytes min bytes max bytes avpkt bytes burst packets [ ecn ] [ bandwidth rate ] probability chance - tc-tbf - tbf - Token Bucket Filter - Traffic shaper to ensure that the configured rate is not exceeded
tc qdisc ... tbf rate rate burst bytes/cell ( latency ms | limit bytes) [ mpu bytes [ peakrate rate mtu bytes/cell ] ] - tc-pfifo / tc-bfifo - The pfifo and bfifo qdiscs are low overhead First In, First Out queues.
- pfifo - Packet limited First In, First Out queue:
tc qdisc ... add pfifo [ limit packets ] - bfifo - Byte limited First In, First Out queue
tc qdisc ... add bfifo [ limit bytes ]
- pfifo - Packet limited First In, First Out queue:
- tc-pfifo_fast - default qdisc of each interface - three-band first in, first out queue
- tc-stab - Generic size table manipulations
tc qdisc add ... stab [ mtu BYTES ] [ tsize SLOTS ] [ mpu BYTES ] [ overhead BYTES ] [ linklayer TYPE ] ...
TCNG:
The goals of tcng are provide a network configuration language. Tcng takes input from a script to be parsed and actions delegated to lower level components and to eventual kernel module directives.
tcng home page
Install:
Ubuntu/Debian: apt-get install tcng
- tcng - Traffic Control New Generation - show or manipulate network traffic control settings
- tcpdump - dump traffic on a network. See discussion below.
Command line option Description -c Exit after receiving count packets. -C Specify size of output dump files. -i Specify interface if multiple exist. Lowest used by default. i.e. eth0 -w file-name Write the raw packets to file rather than parsing and printing them out.
They can later be printed with the -r option.-n Improve speed by not performing DNS lookups. Report IP addresses. -t Don't print a timestamp on each dump line.
Filter expressions:primitive Description host host-name If host has multiple IP's, all will be checked. net network-number Network number. net network-number mask mask Network number and netmask specified. port port-number Port number specified. tcp Sniff TCP packets. udp Sniff UDP packets. icmp Sniff icmp packets. Examples:
- tcpdump tcp port 80 and host server-1
- tcpdump ip host server-1 and not server-2
- iptraf - Interactive Colorful IP LAN Monitor
- nmap - Network exploration tool and security scanner
- List pingable nodes on network: nmap -sP 192.168.0.0/24
Scans network for IP addresses 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.0.255 using ping.
- List pingable nodes on network: nmap -sP 192.168.0.0/24
- Wireshark - Network protocol analyzer. Examine data from a live network.
RPM's required:- wireshark
- wireshark-gnome
- Also: gtk+, glib, glibc, XFree86-libs-x.x.x-x (base install)
- EtherApe - Graphical network monitor for Unix modeled after etherman. This is a great network discovery program with cool graphics.
- Gkrellm - Network and system monitor. Good for monitoring your workstation.
- IPTraf - ncurses-based IP LAN monitor.
- Cheops - Network discovery, location, diagnosis and management. Cheops can identify all of the computers that are on your network, their IP address, their DNS name, the operating system they are running. Cheops can run a port scan on any system on your network.
- ntop - Shows network usage in a way similar to what top does for processes. Monitors how much data is being sent and received on your network.
- MRTG - Multi Router Traffic Grapher - Monitor network traffic load using SNMP and generate an HTML/GIF report.
- dnsad - IP traffic capture. Export to Cisco Netflow for network analysis reporting.
- Big Brother - Monitoring ans services availability.
- OpenNMS.org - Network Management using SNMP.
- Nagios - host, service and network monitoring
- Angel network monitor
Using tcpdump to monitor the network:
[root]# ifconfig eth0 promisc - Put nic into promiscuous mode to sniff traffic.
[root]# tcpdump -n host not XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX | more - Sniff net but ignore IP which is your remote session.
[root]# ifconfig eth0 -promisc - Pull nic out of promiscuous mode.
SNORT: Monitor the network, performing real-time traffic analysis and packet logging on IP networks for the detection of an attack or probe.
- InterSect Alliance - Intrusion analysis. Identifies malicious or unauthorized access attempts.
Ethernet hosts use the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to convert a 32-bit internet IP addresses into a 48-bit Ethernet MAC address used by network hardware. (See: RFC 826) ARP broadcasts are sent to all hosts on the subnet by the data transmitting host to see who replies. The broadcast is ignored by all except the intended receiver which recognizes the IP address as its own. The MAC addresses are remembered (ARP cache) for future network communications. Computers on the subnet typically keep a cache of ARP responses (typically 20 min but can store permanent information for diskless nodes). ARP broadcasts are passed on by hubs and switches but are blocked by routers.
Reverse ARP (See: RFC 903) is a bootstrap protocol which allows a client to broadcast requesting a server to reply with its IP address.
View ARP tables:
- Command /sbin/arp
- Shows other systems on your network (including IP address conflicts): /sbin/arp -a
- Show ARP table Linux style: /sbin/arp -e
- List ARP table: cat /proc/net/arp
- Command /sbin/ip
- Shows other systems on your network (including IP address conflicts): /sbin/ip neigh show
Set/Configure ARP tables:
- Command /sbin/arp
- Add a host's IP address: /sbin/arp -s hostname XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX pub
- Delete a host from the table: /sbin/arp -d hostname
This can be used to remove a duplicate IP or force a new interface to provide info.
- Command /sbin/ip
- Add new ARP entry: ip neigh add 192.168.10.12 lladdr f8:e4:30:38:1c:13 dev eth0 nud perm
(Format: ip neigh add {IP-HERE} lladdr {MAC/LLADDRESS} dev {DEVICE} nud {STATE})
Where STATE:- permanent/perm: The neighbour entry is valid forever and can be only be removed administratively
- noarp: No attempts to validate this entry will be made
- stale: The neighbour entry is valid but suspicious
- reachable: The neighbour entry is valid until the reachability timeout expires
- Delete a ARP entry: ip neigh del 192.168.10.15 dev eth0
- Flush ARP entry: ip -stats neigh flush 192.168.10.5
- Add new ARP entry: ip neigh add 192.168.10.12 lladdr f8:e4:30:38:1c:13 dev eth0 nud perm
Man pages:
- arp (8) man page - manipulate the system ARP cache
- arpwatch (8) man page - keep track of ethernet/ip address pairings
- arpsnmp (8) man page - keep track of ethernet/ip address pairings. Reads information generated by snmpwalk
- arping (8) man page - send ARP REQUEST to a neighbor host
Print ARP reply (similar to arp -a): arping 192.168.10.99 - ip (8) man page - show / manipulate routing, devices, policy routing and tunnels
View ARP table: ip neighbor
ARP is something that simply works. No Linux system configuration is necessary. It's all part of the ethernet and IP protocol. The aforementioned information is just part of the Linux culture of full visibility into what is going on.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a network transport Internet Protocol (IP) typically used for its bi-directional communications reliability. TCP is a protocol which first establishes a connection and then transmits data over that connection. Replies of acknowledgement are sent to each end of the connection to communicate the fact that the transmitted data was valid to determine if the data should be re-sent. The TCP header is 24 bytes of information including the source and destination port, the packet sequence information, checksum and various flags indicating the purpose of the packet. TCP is a streaming protocol where a numbered set of packets are sent over the network and available to the system in-order. This makes TCP appropriate for file transfer and web content delivery.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a protocol which supports a single packet of data with no response, verification or acknowledgement. A checksum is included in the UDP packet header but the protocol does not arrange for retransmission upon error. It is a faster communications method as it does not require the overhead of a connection, reliability or packet order. Each packet is independent of the other and typically used for data no larger than the maximum UDP packet size of 64 Kb (65507 bytes) for the 8 byte header and data, but typically much smaller.
TCP:
| Source Port 16 bits (0 - 65535) |
Destination Port 16 bits (0 - 65535) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sequence Number 32 bits (0 - 4294967295) Increments from 1, zero to clear. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acknowledgement Number 32 bits (0 - 4294967295) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Data Offset |
Res | N S |
C W R |
E C E |
U R G |
A C K |
P S H |
R S T |
S Y N |
F I N |
Window 16 bits |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Checksum 16 bits |
Urgent Pointer (If URG is set) 16 bits |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Options | Padding | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Flags:
- SYN: signifies first packet sent when opening a connection
- ACK: After SYN packet is sent, ACK is set to 1
- RST: Request to reset the connection
- FIN: Last packet - transmission done
UDP:
| Source Port 16 bits (0 - 65535) |
Destination Port 16 bits (0 - 65535) |
||||||||
| Length (entire datagram: header and data) 16 bits (8 - 65535) |
Checksum (If not used - all zeros) 16 bits |
||||||||
Regular network exchanges of data are peer to peer unicast transactions. An HTTP request to a web server (TCP/IP), email SNMP (TCP/IP), DNS (UDP), FTP (TCP/IP), ... are all peer to peer unicast transactions. If one wants to transmit a video, audio or data stream to multiple nodes with one transmission stream instead of multiple individual peer to peer connections, one for each node, one may use multicasting to reduce network load. Note that multicast and a network broadcast are different and that multicast is a UDP broadcast only. Multicast messages are only "heard" by the nodes on the network that have "joined the multicast group" which are those that are interested in the information.
The Linux kernel is Level-2 Multicast-Compliant. It meets all requirements to send, receive and act as a router for multicast datagrams. For a process to receive multicast datagrams it has to request the kernel to join the multicast group and bind the port receiving the datagrams. When a process is no longer interested in the multicast group, a request is made to the kernel to leave the group. It is the kernel/host which joins the multicast group and not the process. Kernel configuration requires "CONFIG_IP_MULTICAST=y". In order for the Linux kernel to support multicast routing, set the following in the kernel config:
- CONFIG_IP_MULTICAST=y
- CONFIG_IP_ROUTER=y
- CONFIG_IP_MROUTE=y
- CONFIG_NET_IPIP=y
The default Red Hat / Fedora kernels are compiled to support multicast.
See the YoLinux tutorial on optimization and rebuilding the Linux kernel.
Note that on multihomed systems (more than one IP address/network card), only one device can be configured to handle multicast.
Class D networks with a range of IP addresses from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 (See Network Classes above) have typically been reserved for multicast.
Useful commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| cat /proc/net/igmp | List multicast group to which the host is subscribed. Use "Internet Group Management Protocol". (See /usr/src/linux/net/core/igmp.c) |
| cat /proc/net/dev_mcast | List multicast interfaces. (See /usr/src/linux/net/core/dev_mcast.c) |
| ping 224.0.0.1 | All hosts configured for multicast will respond with their IP addresses |
| ping 224.0.0.2 | All routers configured for multicast will respond |
| ping 224.0.0.3 | All PIM routers configured for multicast will respond |
| ping 224.0.0.4 | All DVMRP routers configured for multicast will respond |
| ping 224.0.0.5 | All OSPF routers configured for multicast will respond |
Multicast transmissions are achieved through proper routing, router configuration (if communicating through subnets) and programatically with the use of the following "C" function library calls:
| Function Call | Description |
|---|---|
| setsockopt(int sockfd, int level, int optname, const void* optval, socklen_t optlen) | Pass information to the Kernel. |
| getsockopt(int sockfd, int level, int optname, void *optval, socklen_t *optlen) | Retrieve information broadcast using multicast. |
Where optname is:
| Option | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IP_MULTICAST_IF | 32 | Specify ethernet interface to use:struct in_addr interface_addr;Can use setsockopt() with option INADDR_ANY to reset the configuration. |
| IP_MULTICAST_TTL | 33 | Time To Live (TTL) value sets how many router hops are allowed. Restrict to local network: u_char ttl = 1;Values of ttl are 0 to 255 |
| IP_MULTICAST_LOOP | 34 | Data sent is looped back to the same host. Enable: uchar loop = 1where loop=0 to disable loopback |
| IP_ADD_MEMBERSHIP | 35 | Specify multicast group. Include file linux/in.h set struct ip_mreq
setsockopt (socket, IPPROTO_IP, IP_ADD_MEMBERSHIP, &mreq, sizeof(mreq));Add as many groups as needed. |
| IP_DROP_MEMBERSHIP | 36 | Closing the socket will drop membership or: struct ip_mreq mreq; setsockopt (socket, IPPROTO_IP, IP_DROP_MEMBERSHIP, &mreq, sizeof(mreq)); |
| IP_UNBLOCK_SOURCE | 37 | Unblock a previously blocked source for a given multicast group. |
| IP_BLOCK_SOURCE | 38 | Block IPv4 multicast packets that have a source address that matches the given IPv4 source address. |
| IP_ADD_SOURCE_MEMBERSHIP | 39 | Join IPv4 multicast group on an IPv4 interface and specify the IPv4 source-filter address. Set these values by using the SETSOCKOPT API. |
| IP_DROP_SOURCE_MEMBERSHIP | 40 | Drop multicast group. |
| IP_MSFILTER | 41 | |
| MCAST_JOIN_GROUP | 42 | Join a multicast group and set the IPv4 or IPv6 multicast address and the local interface. |
| MCAST_BLOCK_SOURCE | 43 | |
| MCAST_UNBLOCK_SOURCE | 44 | |
| MCAST_LEAVE_GROUP | 45 | Leave a multicast group. |
| MCAST_JOIN_SOURCE_GROUP | 46 | |
| MCAST_LEAVE_SOURCE_GROUP | 47 | |
| MCAST_MSFILTER | 48 | |
| IP_MULTICAST_ALL | 49 |
The multicast application will specify the multicast group, loopback interface, TTL (network time to live or router hops), network interface and the multicast group to add or drop.
Add route to support multicast:- /sbin/ifconfig eth0 multicast
- route -n add -net 224.0.0.0 netmask 240.0.0.0 dev eth0
- /sbin/ip route show (show the route you just created)
Linux can be configured to forward packets and act as a simple router between two networks. The prior section on "Enable Forwarding" shows how Linux can be configured to forward regular TCP and UDP packets. This does not include multicast packets.
Multicasting begins with an application requesting multicast group membership. It is this request that tells a muliticast router to enable forwarding on the interface that the request arrived on -- no request, no routing. The request must be processed by a multicasting router. Multicast packets can be forwarded and routed by running multicast routing software on the system.
| Routing software | Protocols | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Xorp | PIM | Routing of IPv4 and IPv6 network protocols including UDP multicast |
| SmcRoute | PIM | Simple static routing of UDP multicast |
| mrouted | DVMRP | DVMRP (Distance Vector Multicast Protocol) is a depricated protocol thus making this software obsolete. |
| pimd | PIM PIM-SM: PIM Sparse Mode PIM-DM: PIM Dense Mode | Supports PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast) routing protocol. |
| Quagga | PIM BGP-4 RIP OSPFv2i, etc | Quagga (a fork of Zebra) is a routing application supporting a full range of routing protocols. |
Linux can support Internet Protocol (IP) protocol over serial device interfaces. Over long distances this is typically supported using a modem over telephone lines (POTS: Plain Old Telephone Service) or satellite communications.
This is the most common form of IP over serial line and is the most common technique used by telephone dial-up ISPs. The following tutorials use a Hayes command set compatible modem.
- YoLinux Tutorial: Configuring PPP dial up connections to an ISP
- YoLinux Tutorial: Dialing Compuserve
- YoLinux Tutorial: Dialing AOL
- RFC 2637: Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP).
- PPTP-Linux Client - A PPTP Linux client that allows a linux system to connect to a PPTP server. Developed by C. S. Ananian.
- Counterpane Systems FAQ on Microsoft's PPTP Implementation - FAQ on the security flaws in Microsoft's PPTP Implementation.
Devices:
| Interfaces | Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sl0 | sl1 | sl2 | sl3 | SLIP interfaces. Linux kernel supports up to four. |
| COM1 | COM2 | COM3 | COM4 | Serial Ports (RS-232 hardware) |
| /dev/ttyS0 | /dev/ttyS1 | /dev/ttyS2 | /dev/ttyS3 | Serial devices (dial in) (virtual terminal consoles) |
| /dev/cua0 | /dev/cua1 | /dev/cua2 | /dev/cua3 | Serial devices (dial out) |
| 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Interface major numbers (dial in) |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Interface major numbers (dial out) |
| 64 | 65 | 66 | 67 | Interface minor numbers |
The major and minor numbers are used when creating a SPLIP interface:
Example:
- mknod -m 666 /dev/cua1 c 5 65
- chown root.uucp /dev/cua1
- Configure /etc/resolv.conf
(See notes above in this tutorial) - Attach network interface to serial line on COM2: /sbin/slattach -p slip -s 19200 /dev/ttyS1 &
- Assign local and remote IP: /sbin/ifconfig sl0 192.168.1.10 pointopoint 192.168.1.40 up
Assign local IP (192.168.1.10) and connect to remote server (192.168.1.40)
Alternate example: /sbin/route add plip1 192.168.1.10 pointopoint 192.168.1.40 - Add route: /sbin/route add default dev sl0 &
Point to point serial links (rather than broadcast networks line ethernet), can also be supported over parallel printer ports.
An IP network at 10 to 20 kBps over parallel printer ports lp0 or lp1 are much faster than serial. Linux supports mode 0 PLIP transferring half bytes of data at a time. Requires "NULL Printer" or "Turbo Laplink" printer connection. See kernel source drivers/net/Space.c.| Interface | I/O Port | IRQ |
|---|---|---|
| plip0 | 0x3BC | 7 |
| plip1 | 0x378 | 7 |
| plip2 | 0x278 | 5 |
- ifconfig plip1 192.168.1.10 pointopoint 192.168.1.40
connect host 192.168.1.10 to remote host 192.168.1.40 - route add default gw 192.168.1.40
Specify remote host as the gateway.
- ifconfig plip1 192.168.1.40 pointopoint 192.168.1.10
- route add 192.168.1.10 gw 192.168.1.40
- setserial - get/set Linux serial port information
Typical configuration:- Interrupt detection: /sbin/setserial -W /dev/cua*
- Configuration: /sbin/setserial /dev/cua1 auto_irq skip_test autoconfig
or /sbin/setserial /dev/cua1 auto_irq skip_test autoconfig uart 16550 - Display Configuration: /sbin/setserial -bg /dev/cua*
- Enable hardware handshake: stty crtscts < /dev/cua1
(verify: stty -s < /dev/cua1)
- stty - change and print terminal line settings
- tty - print the file name of the terminal connected to standard input
- pppd - Point-to-Point Protocol Daemon
- slattach - attach a network interface to a serial line
- mknod - make block or character special files
- SMB4k: My favorite MS/Windows file share browser.
- In Nautilus use the URL "smb:" to view MS/Windows servers. [tutorial]
See the YoLinux tutorial on integrating Linux into a Microsoft network.
- IPv4: Most of the Internet servers and personal computers use Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4). This uses 32 bits to assign a network address as defined by the four octets of an IP address up to 255.255.255.255. Which is the representation of four 8 bit numbers thus totaling 32 bits.
- IPv6: Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) uses a 128 bit address and thus billions and billions of potential addresses. The protocol has also been upgraded to include new quality of service features and security. Currently Linux supports IPv6 but IPv4 is used when connecting your computer to the internet.
- TCP/IP: (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) uses a client - server model for communications. The protocol defines the data packets transmitted (packet header, data section), data integrity verification (error detection bytes), connection and acknowledgement protocol, and re-transmission.
- TCP/IP time to live (TTL): This is a counting mechanism to determine how long a packet is valid before it reaches its destination. Each time a TCP/IP packet passes through a router it will decrement its TTL count. When the count reaches zero the packet is dropped by the router. This ensures that errant routing and looping aimless packets will not flood the network.
- MAC Address: (media access control) is the network card address used for communication between other network devices on the subnet. This info is not routable. The ARP table maps TCP/IP address (global internet) to the local hardware on the local network. Use the command /sbin/ifconfig to view both the IP address and the MAC address. The MAC address uniquely identifies each node of a network and is used by the Ethernet protocol.
- Full Duplex: Allows the simultaneous sending and receiving of packets. Most modern modems support full duplex.
- Half Duplex: Allows the sending and receiving of packets in one direction at a time only.
- OSI 7 Layer Model: The ISO (International Standards
Organization) has defined the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model
for current networking protocols.
OSI Layer Description Linux Networking Use 7 Application Layer.
The top layer for communications applications like email and the web.telnet, web browser, sendmail 6 Presentation Layer.
Syntax and format of data transfer.SMTP, http 5 Session Layer.
4 Transport Layer.
Connection, acknowledgement and data packet transmission.TCP
UDP3 Network Layer. IP
ARP2 Data Link Layer.
Error control, timingEthernet 1 Physical Layer.
Electrical characteristics of signal and NICEthernet - Network Hub: Hardware to connect network devices together. The devices will all be on the same network and/or subnet. All network traffic is shared and can be sniffed by any other node connected to the same hub.
- Network Switch: Like a hub but creates a private link between any two connected nodes when a network connection is established. This reduces the amount of network collisions and thus improves speed. Broadcast messages are still sent to all nodes.
- Cable modem HowTo - Vladimir Vuksan
- Ethernet HowTo - Paul Gortmaker
- YoLinux Tutorial: Setting up an internet gateway for home or office using iptables or ipchains
- Firewall HowTo - Mark Grennan
- YoLinux networking tutorial
- Networking Overview HowTo - Daniel Lopez Ridruejo
- Networking Howto - Joshua Drake
- NFS Howto - Nicolai Langfeldt
- SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol (Uses ports 161,162,391,1993)
- SNMP - Intro tutorials
- Linux SNMP Network Management Tools
- SNMP FAQ
- net-snmp - tools and libraries
- News/Usenet Group: comp.os.linux.networking - Deja
- MARS-nwe - Netware emulator
- Linux 2.4 Advanced Routing HOWTO - iproute2, traffic shaping and a bit of netfilter
- ISDN:
- ISDN4LINUX FAQ - Matthias Hessler
- ISDN4 Linux Home Page
- DHCP: (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
- YoLinux DHCP Tutorial - How to set up a DHCP server.
- ISC Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - DHCP home page
- Multicast:
- YoLinux Tutorial: Configuring Linux for multicast - this tutorial in section above
- Multicast over TCP/IP HOWTO
- ISP's: (National/Global)
- TheList.com - Comprehensive list of ISP's
- Concentric
- NIS: (NFS infrastructure)
- YoLinux NIS tutorial - NIS configuration and use
- NIS howto
- Ethernet cables:
- VIX: Vienna Internet eXchange - European traffic exchange for ISP's
Test Internet Bandwidth:
More Networking Man Pages:
- icmp - Linux IPv4 ICMP kernel module
- usernetctl - allow a user to manipulate a network interface if permitted
- SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol (query/configure network devices)
(RH/CentOS packages net-snmp and net-snmp-utils)- snmpd - daemon to respond to SNMP request packets
- /etc/snmp/snmp.conf - configuration file for Net-SNMP applications
- snmpconf - creates and modifies SNMP configuration files
- snmpstatus - retrieves a fixed set of management information from a network entity
- snmptrap - sends an SNMP notification to a manager
- snmpnetstat - display networking status and configuration information from a network entity via SNMP
- snmptest - communicates with a network entity using SNMP requests
- snmpcmd - options and behaviour common to most of the Net-SNMP commandline tools
snmpcmd [OPTIONS] AGENT [PARAMETERS] - snmpset - communicates with a network entity using SNMP SET requests
snmpset [COMMON OPTIONS] OID TYPE VALUE [OID TYPE VALUE]... - snmpget - communicates with a network entity using SNMP GET requests
snmpget [COMMON OPTIONS] [-Cf] OID [OID]... - variables - Format of specifying variable names to SNMP tools


 Books:
Books:




















